Oracle Data Sharing & Security
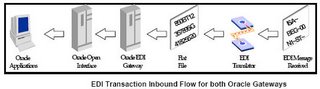
| Executive Summary In today’s business environment, where division of labor is present all around and tasks are highly specialized, it becomes imperative for any organization to make sure that users have access to data that is relevant only to them to carry out their specified task. Businesses have to make sure that not only the relevant data is available to the users but the data is also secure. This can become quite a challenging and complex job to manage given that there are users at different level of organization, who require different levels of access, and there can be multiple systems that can be used to access data. For example, there can be a requirement that the ‘Bill To’ address of a customer can only be updated by the legal department or the customer service department should not be allowed to create, update or delete customer’s (organization party) legal name and address. Such requirements can be the result of an organization’s attempt to be SOX compliant or as a result of corporate policy. Given this, it becomes quite a complex, but necessary job to make sure that users have access to the right data with optimal security. Oracle released this much needed functionality of ‘Data Sharing and Security’ (DSS) in Oracle Customers Online, release 11.5.9 (IMC.J). This functionality gives the implementing organization a tool to centrally manage data security. System administrators can setup up data sharing groups that can be used to determine which user or responsibility has privileges to create, update, or delete data. Before this release the most common way to exercise control over data was through menu customizations where in most cases users could either have full access or not have any access at all. This paper attempts to explain the concepts of DSS (including how the DSS logic works) and illustrates in detail how an implementing organization can setup DSS to achieve data security. Data Sharing & Security (DSS) Concepts 1. To turn on DSS, system profile ‘HZ: Data Sharing and Security Enabled’ should be set to ‘Yes’ at the site level. Doing so will make all the responsibilities read only. After this, individual security groups can be created and responsibilities can be assigned create, update, or delete privileges for various TCA entities. 2. DSS provides row level security where a user can create, update, or delete a row in the table. It does not provide column level security where a user can create, update, or delete a particular column (attribute) in a row. For example, if a user is allowed to create party address the he / she will be allowed to populate all the columns in the address row. User cannot have create privilege for just Address2 and City columns. 3. Create, update, or delete privileges can be assigned to: a. User (individual users level) b. Group (responsibility level) c. Public (all users) 4. Privileges consist of ability to: a. Create b. Update c. Delete 5. DSS provides ranking to prioritize data access. For example, if a party falls under two or more classifications then this conflict can be addressed by ranking a DSS group with one classification higher than the DSS group with another classification or assigning a combination of classifications to different DSS groups. 6. Person parties that gets created by HR module can only be modified by a user who is also an authorized HRMS user. Defining A Data Sharing Group The following attributes can be secured in a DSS group: 1. Classifications: By default, users and responsibilities are allowed to create, update and delete (depending on boxes checked in ‘Assignment’) records for all the seeded and custom classifications. By selecting particular classification(s) in this region, one can specify that the user and responsibility are allowed to create, update and delete the record which has this classification(s). It’s like adding a where clause. For example, if the DSS group has a classification of ‘GSA’ and the ‘Organization Party, Address and Contact Points entities are checked, then the associated responsibility can update only the party which has ‘GSA’ classification. 2. Relationship: By default users and responsibilities are allowed to create, update and delete (depending on boxes checked in ‘Assignment’) records for all the relationship roles. By selecting particular relationship roles in this region, one is specifying that the user and responsibility is allowed to create, update and delete the record which has this relationship role(s). It’s like adding a where clause. For example, if a DSS group has a relationship role of ‘Division’ and the relevant privileges are checked, then the associated responsibility can create, update and delete only the party which has a ‘Division’ relationship role. 3. Created By Module: By default the DSS group pertains to all the modules. However, by selecting a particular module(s), users can say that the DSS holds true as long the record is being created, updated and deleted by this module(s). This refers to the ‘Who’ column in the table. Who created the record? It’s like adding a where clause. For example, if the DSS group has the ‘Created By Module’ TCA_V1_API (OCO) and the associated responsibility is of Order Management then the user will not be able to create, update and delete the record. 4. Entities: a. Person Parties b. Organization Parties c. Party Contact Points d. Party Site Contact Points e. Classification Code Assignments f. Relationships g. Parties h. Party Address The above entities can be selected to give a user and a responsibility privileges to create, update and delete any record with the checked entities. DSS Basic Process DSS Basic Process Legend Process Decision Process Start/End Create, Update, or Delete Box Checked? No Yes Select DSS Group With Highest Ranking Yes Select DSS Groups With Matching Entity Responsibility Exists? No Action Not Allowed Create, Update, or Delete Record Record Created, Updated, or Deleted Action Not Allowed DSS Logic & Setup Illustration Below is logic that the Data Sharing and Security module uses. The illustration below can also be used by an implementing organization as guidelines to implement DSS as per its needs. Requirements # Responsibility Description 1 OCO Organization Only This responsibility should allow creating, updating and deleting only organization and its attributes (profiles). 2 Sales User This responsibility should not allow creating, updating, and deleting organizations and their attributes. This should only allow creating, updating and deleting party contacts. 3 OCO User This responsibility should not have any restrictions. Should allow creating, updating, and deleting any record. 4 Inquiry Only This responsibility should make the application read only. Should not allow creating, updating, and deleting any record. Data Sharing Groups Rank Name Description Enabled 1 Create Organization Only Create Organization Only Yes 2 Create Contact Only Create Contact Only Yes 3 Inquiry Only Inquiry Only Yes 4 Human Resources Shared Data* Human Resources Shared Data Yes 5 Public* Public Yes * Already comes setup with the application. Setup Details of Each DSS group ‘Create Organization Only’ Data Sharing Group Field Value Data Sharing Group Name Create Organization Only Data Sharing Group Code CREATE_ORGANIZATION_ONLY Data Sharing Group Description Create Organization Only Rank 1 Entities Name Selected Parties Person parties Organization Parties Yes Relationships Classification Code Assignments Party Contact Points Party Site Contact Points Party Addresses Assign Privileges Type of Grantees Name Create Update Delete Group OCO Organization Only Yes Yes Yes Group OCO Users Yes Yes Yes ‘Create Contact Only’ Data Sharing Group Field Value Data Sharing Group Name Create Contact Only Data Sharing Group Code CREATE_CONTACT_ONLY Data Sharing Group Description Create Contact Only Rank 2 Entities Name Selected Parties Person parties Yes Organization Parties Relationships Classification Code Assignments Party Contact Points Party Site Contact Points Party Addresses Assign Privileges Type of Grantees Name Create Update Delete Group Sales User Yes Yes Yes Group OCO User Yes Yes Yes ‘Inquiry Only’ Data Sharing Group Field Value Data Sharing Group Name Inquiry Only Data Sharing Group Code INQUIRY_ONLY Data Sharing Group Description Inquiry Only Rank 3 Entities Name Selected Parties Yes Person parties Yes Organization Parties Yes Relationships Yes Classification Code Assignments Yes Party Contact Points Yes Party Site Contact Points Yes Party Addresses Yes Assign Privileges Type of Grantees Name Create Update Delete Group Sales User Yes Yes Yes Group OCO Organization Only Yes Yes Yes Group Inquiry Only Responsibility - OCO Organization Only Scenario I – Create Organization User creates an organization or updates an organization. The record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have ‘Organization Parties’ entity checked. 2. Ranking of these DSS groups. The record will select the following DSS groups with Organization Party entity checked. 1. Create Organization Only 2. OCO Inquiry 3. Public Since ‘Create Organization Only’ DSS group has a higher ranking (1) as compared to ‘OCO Inquiry’ (3) and ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the first DSS ‘Create Organization Only’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘OCO Organization Only’ responsibility and the ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked therefore, the system will allow the record to be created. Scenario I a – Creating Contact Points To create an organization, the system must be able to create a ‘Party Address’ and optionally ‘Contact Points’. Therefore, the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entity checked. a. Party Contact Points b. Party Site Contact Points c. Party Addresses 2. Ranking of these groups. To process address and contact points, the record will select the following DSS groups with above 1a, 1b, 1c entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the third DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘OCO Organization Only’ responsibility and ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked, therefore, the system will allow address and contact points records to be created. Scenario II – Create Person / Contact Party If the user tries to create or update a contact using this responsibility then the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have ‘Person Parties’ entity checked. 2. Ranking of these DSS groups. The record will select the following DSS groups with Organization Party entity checked. 1. Create Contact Only 2. OCO Inquiry 3. Public Since ‘Create Contact Only’ DSS group has a higher ranking (2) as compared to ‘OCO Inquiry’ (3) and ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the second DSS ‘Create Contact Only’ and look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS does not have ‘OCO Organization Only’ responsibility therefore, the system will not allow the record to be created. Responsibility - Sales User Scenario I – Create Organization User creates an organization or updates an organization. The record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have ‘Organization Parties’ entity checked. 2. Ranking of these DSS groups. The record will select the following DSS groups with Organization Party entity checked. 1. Create Organization Only 2. OCO Inquiry 3. Public Since ‘Create Organization Only’ DSS group has a higher ranking (1) as compared to ‘OCO Inquiry’ (3) and ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the first DSS ‘Create Organization Only’ and look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS does not have ‘Sales User’ responsibility therefore, the system will not allow the record to be created. Scenario II – Create Person / Contact Party If the user tries to create or update a contact (including contact points etc) using this responsibility then the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entity checked. a. Person parties b. Relationships c. Party Contact Points d. Party Site Contact Points e. Party Addresses 2. Ranking of these DSS groups. To process the person party record, the record will select the following DSS groups with ‘Person Parties’ entity checked. 1. Create Contact Only 2. OCO Inquiry 3. Public Since ‘Create Contact Only’ DSS group has a higher ranking (2) as compared to ‘OCO Inquiry’ (3) and ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the second DSS ‘Create Contact Only’ and look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘Sales User’ responsibility and ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked, therefore, the system will allow the record to be created. Scenario II a – Creating Party Relationship To create a contact, the system must be able to create a ‘Relationship’. Therefore, the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have ‘Relationship’ entity checked. 2. Ranking of these groups. To process ‘Relationship’, the record will select the following DSS groups with ‘Relationships’ entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the second DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘Sales User’ responsibility and ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked, therefore, the system will allow the relationship record to be created. Scenario II b – Creating Contact Points To create a contact, the system must be able to create a ‘Party Address’ and optionally ‘Contact Points’. Therefore, the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entity checked. a. Party Contact Points b. Party Site Contact Points c. Party Addresses 2. Ranking of these groups. To process ‘Contact Points’, the record will select the following DSS groups with 1a, 1b, 1c entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the second DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘Sales User’ responsibility and ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked, therefore, the system will allow the relationship record to be created. Responsibility - OCO User Scenario I – Create Organization User creates an organization or updates an organization. The record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have ‘Organization Parties’ entity checked. 2. Ranking of these DSS groups. The record will select the following DSS groups with Organization Party entity checked. 1. Create Organization Only 2. OCO Inquiry 3. Public Since ‘Create Organization Only’ DSS group has a higher ranking (1) as compared to ‘OCO Inquiry’ (3) and ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the first DSS ‘Create Organization Only’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘OCO User’ responsibility and the ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked therefore, the system will allow the record to be created. Scenario I a – Creating Contact Points To create an organization, the system must be able to create a ‘Party Address’ and optionally ‘Contact Points’. Therefore, the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entity checked. a. Party Contact Points b. Party Site Contact Points c. Party Addresses 2. Ranking of these groups. To process address and contact points, the record will select the following DSS groups with above 1a, 1b, 1c entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the third DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘OCO User’ responsibility and ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked, therefore, the system will allow address and contact points record to be created. Scenario II – Create Person / Contact Party If the user tries to create / update a contact (including contact points etc) using this responsibility then the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entity checked. a. Person parties 2. Ranking of these DSS groups. To process the person party record, the record will select the following DSS groups with ‘Person Parties’ entity checked. 1. Create Contact Only 2. OCO Inquiry 3. Public Since ‘Create Contact Only’ DSS group has a higher ranking (2) as compared to ‘OCO Inquiry’ (3) and ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the second DSS ‘Create Contact Only’ and look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘OCO User’ responsibility and ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked, therefore, the system will allow the person record to be created. Scenario II a – Creating Party Relationship To create a contact, the system must be able to create a ‘Relationship’. Therefore, the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have ‘Relationship’ entity checked. 2. Ranking of these groups. To process ‘Relationship’, the record will select the following DSS groups with ‘Relationships’ entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the third DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS has ‘OCO User’ responsibility and ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked, therefore, the system will allow the relationship record to be created. Scenario II b – Creating Contact Points To create a contact, the system must be able to create a ‘Party Address’ and optionally ‘Contact Points’. Therefore, the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entity checked. a. Party Contact Points b. Party Site Contact Points c. Party Addresses 2. Ranking of these groups. To process ‘Contact Points’, the record will select the following DSS groups with 1a, 1b, 1c entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the third DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this group has ‘OCO User’ responsibility and ‘Create’, ‘Update’, and ‘Delete’ boxes are checked, therefore, the system will allow the relationship record to be created. Responsibility - OCO Inquiry Scenario I – Create Organization User creates an organization or updates an organization. The record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have ‘Organization Parties’ entity checked. 2. Ranking of these DSS groups. The record will select the following DSS groups with Organization Party entity checked. 1. Create Organization Only 2. OCO Inquiry 3. Public Since ‘Create Organization Only’ DSS group has a higher ranking (1) as compared to ‘OCO Inquiry’ (3) and ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will first select the first DSS ‘Create Organization Only’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this group does not have ‘OCO Inquiry’ responsibility therefore, the record will move to the next DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’. This DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ also does not has ‘OCO Inquiry’ responsibility therefore the system will not allow creation of Organization record. Scenario I a – Creating Contact Points To create an organization, the system must be able to create a ‘Party Address’ and optionally ‘Contact Points’. Therefore, the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entity checked. a. Party Contact Points b. Party Site Contact Points c. Party Addresses 2. Ranking of these groups. To process address and contact points, the record will select the following DSS groups with above 1a, 1b, 1c entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the third DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS does not have ‘OCO Inquiry’ responsibility, therefore, the system will not allow address and contact points record to be created. Scenario II – Create Person / Contact Party If the user tries to create / update a person record using this responsibility then the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entity checked. a. Person parties 2. Ranking of these DSS groups. To process the person party record, the record will select the following DSS groups with ‘Person Parties’ entity checked. 1. Create Contact Only 2. OCO Inquiry 3. Public Since ‘Create Contact Only’ DSS group has a higher ranking (2) as compared to ‘OCO Inquiry’ (3) and ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the second DSS ‘Create Contact Only’ and look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS does not have ‘OCO Inquiry’ responsibility therefore, the system will not allow the person record to be created. Scenario II a – Creating Relationship If the user tries to create any party relationship (organization to organization or organization to person) the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have ‘Relationship’ entity checked. 2. Ranking of these groups. To process ‘Relationship’, the record will select the following DSS groups with ‘Relationships’ entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the third DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS does not have ‘OCO Inquiry’ responsibility, therefore, the system will not allow the relationship record to be created. Scenario II b – Creating Contact Points To create a contact or an organization, the system must be able to create a ‘Party Address’ and optionally ‘Contact Points’. Therefore, the record will look at: 1. All the DSS groups which have the following entities checked. a. Party Contact Points b. Party Site Contact Points c. Party Addresses 2. Ranking of these groups. To process ‘Contact Points’, the record will select the following DSS groups with 1a, 1b, 1c entity checked. 1. OCO Inquiry 2. Public Since ‘OCO Inquiry’ DSS group has a higher ranking (3) as compared to ‘Public’ (5). Therefore, the record will select the third DSS ‘OCO Inquiry’ and then look at the responsibilities. Since this DSS does not have ‘OCO Inquiry’ responsibility, therefore, the system will not allow the relationship record to be created. Note: If a user has responsibility ‘A’, that has privileges to create, update, or delete entities, and responsibility ‘B’ that does not have such privileges then, responsibility ‘A’ will take precedence over responsibility ‘B’ and the user will be allowed to create, update, or delete entities. Therefore, users should not be assigned such responsibilities with contradicting privilege assignments. Limitations of Data Sharing and Security Model 1. No Account Level Protection: OCO introduced the much desired functionality of account level access in 11.5.10 release. But OCO does not have any data security through DSS. Implementing organizations will have to use OA Framework personalization to secure data. For example, if the requirement is that users with ‘Sales User’ responsibility should not be allowed to create account level contact then the only way fulfill this requirement is through removing the ‘Create Contact’ button in the ‘Account Overview’ page through OA Framework personalization. 2. Complete Visibility of All Data: Users can be given create, update and delete privileges through DSS but DSS cannot hide the data from a user. In other words, a user will always be able to see all the data even he / she may not have any privileges to create, update and delete. For example, system administrators will not be able to hide a party of ‘GSA’ classification from certain users. 3. Only Row Level Protection: As mentioned earlier in this paper, DSS can give create, update and delete privileges to the entire row in the table and not to a certain columns for that row. |